41 compare the movement of surface and deep currents
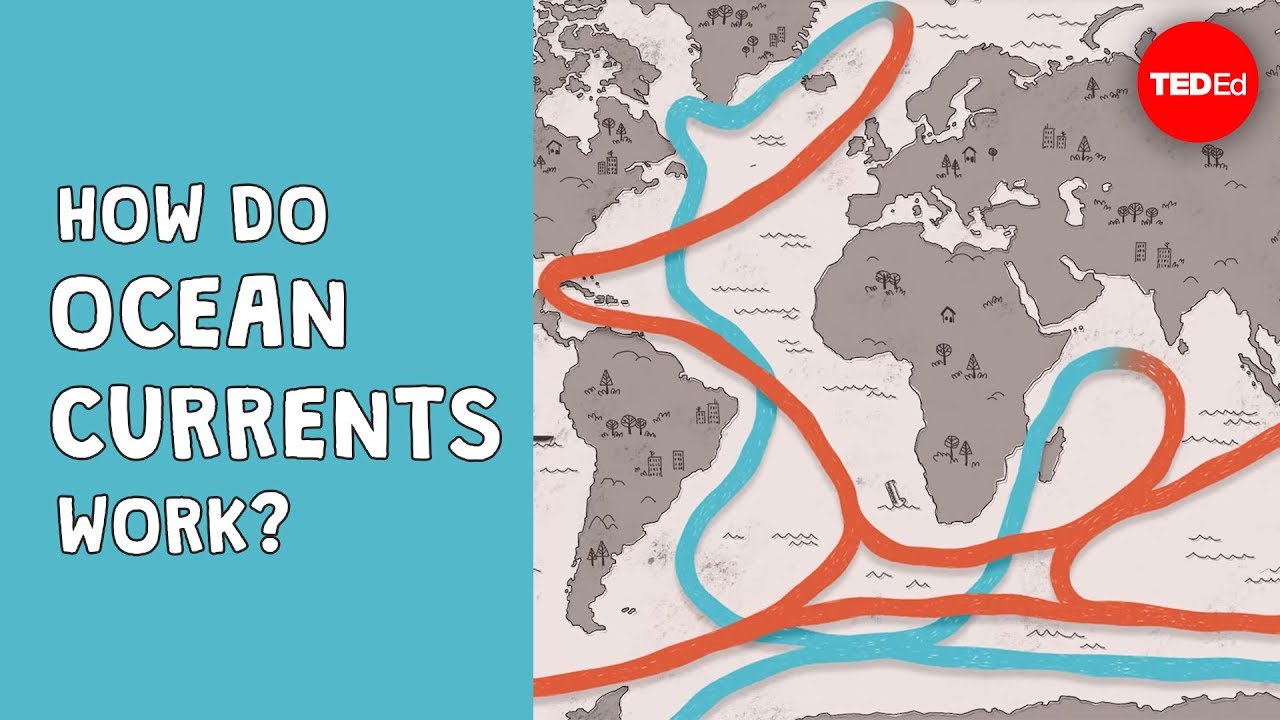
Solutions for all Social Sciences Grade 8 ... - Academia.edu The water in the oceans moves and spreads the heat throughout the oceans, across different parts of the earth. We call this movement of water, ocean currents. The temperature of ocean currents affects the temperature of places next to them. Ocean currents also influence the amount of rain that falls in an area. Currents, Waves, and Tides | Smithsonian Ocean A large movement of water in one general direction is a current. Currents can be temporary or long-lasting. They can be near the surface or in the deep ocean. The strongest currents shape Earth's global climate patterns (and even local weather conditions) by moving heat around the world. Surface Currents
PDF CHAPTER SECTION 1 Currents Not all ocean currents are found at the surface. Movements of ocean water far below the surface are called deep currents. Unlike surface currents, deep currents are not controlled by wind. Deep current move-ments are controlled by water density. Density is the amount of matter in a given space or volume. The density of ocean water is affected by

Compare the movement of surface and deep currents
PDF CHAPTER SECTION 1 Currents - WPMU DEV Not all ocean currents are found at the surface. Movements of ocean water far below the surface are called deep currents. Unlike surface currents, deep currents are not controlled by wind. Deep current move-ments are controlled by water density. Density is the amount of matter in a given space or volume. The density of ocean water is affected by Ocean Surface Currents | manoa.hawaii.edu ... Surface currents are only 50 to 100 meters deep (Table 3.1). Though shallow, they are extremely important in determining the world's weather and climates, and in distributing the ocean's heat and nutrients. Winds are described by the direction from which they blow, whereas water currents are described by the direction toward which they flow. Currents | Earth Science - Lumen Learning Surface currents can flow for thousands of kilometers and can reach depths of hundreds of meters. These surface currents do not depend on weather; they remain unchanged even in large storms because they depend on factors that do not change. Surface currents are created by three things: global wind patterns the rotation of the Earth
Compare the movement of surface and deep currents. Ocean currents- The movement of life ⋆ TheScientificRevelation Ocean currents are the movement of water. They are mainly of two type Surface and Deep ocean currents. Surface currents are found on the surface of the ocean and driven by wind and Coriolis force. On the other hand, deep ocean currents are driven by density difference, salinity, and temperature. Compare and Contrast Deep ocean currents, and surface ... Surface currents are caused by wind blowing across the atlantic. (Affrects the top 30 feet) Surface currents Deep ocean currents Circulate tempature Move in a circular fomation called a Gyre. Colder water sinks and the warmer water rises to the top which helps bring oxygen down to animals at the bottom of the ocean. Show full text 9.5: Currents, Upwelling and Downwelling - LibreTexts The movement of surface currents also plays a role in the vertical movements of deeper water, mixing the upper water column. Upwelling is the process that brings deeper water to the surface, and its major significance is that it brings nutrient-rich deep water to the nutrient-deprived surface, stimulating primary production (see section 7.3). Atoms, Molecules, and Compounds | manoa.hawaii.edu ... Further Investigations: Ocean Surface Currents; Effect of Surface Currents. Climate Connections: Sea Level Rise; Activity: Sea Level and Gravitational Flow; Question Set: Effects of Surface Currents; Further Investigation: Effects of Surface Currents; Climate and Atmosphere. Activity: Climate Comparison; Question Set: Climate and the Atmosphere
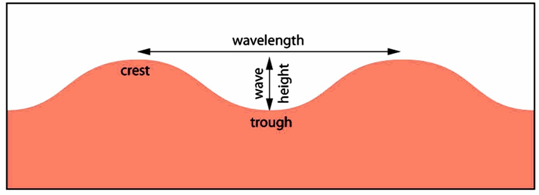
PDF Activity: Ocean Currents There are: Surface currents are driven by wind and follow global atmospheric patterns. Cold surface currents move from the polar regions to the equatorial zones, and warm surface current move in the oppo site way. Deep currents are caused by the differences in water densities. 4th grade Energy & Waves disturbing the surface. When waves move across the surface of deep water, the water goes up and down in place; it does not move in the direction of the wave except when the water meets the beach. • Waves of the same type can differ in amplitude (height of the wave) and wavelength (spacing between wave peaks). 6* ,8 What is the difference between surface current and deep ... Best Answer. Copy. Surface currents depend on temperature and wind which is in the atmosphere but deep water currents do not as it occurs under water. Wiki User. ∙ 2010-03-15 15:52:28. This ... Surface Currents | Physical Geography - Lumen Learning Surface Currents Ocean water moves in predictable ways along the ocean surface. Surface currents can flow for thousands of kilometers and can reach depths of hundreds of meters. These surface currents do not depend on weather; they remain unchanged even in large storms because they depend on factors that do not change.
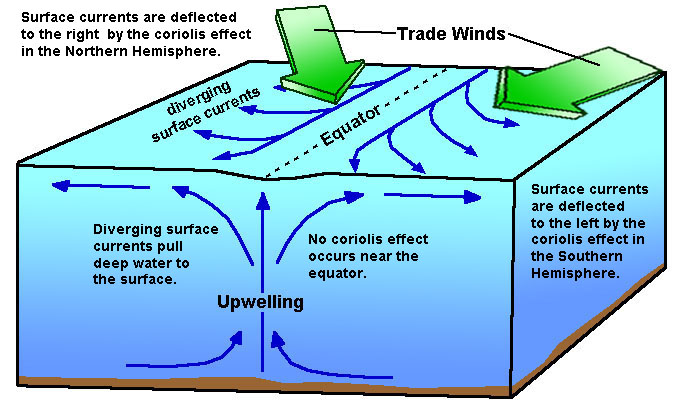
9.5 Currents, Upwelling and Downwelling - Introduction to ... 9.5 Currents, Upwelling and Downwelling. The movement of surface currents also plays a role in the vertical movements of deeper water, mixing the upper water column. is the process that brings deeper water to the surface, and its major significance is that it brings -rich deep water to the nutrient-deprived surface, stimulating. Geo One Test 3 Flashcards - Quizlet The result is a surface flow at 45 degrees to the right of the wind in the Northern Hemisphere. Water at increasing depth below the surface will drift in directions increasingly more slowly and to the right until about 100m depth, it may move in direction opposite to that of the wind. 3 Differences between Sea Waves and Sea Currents ... The differences between sea waves and sea currents is as follows: The direction of mass water movement. The first difference from sea waves and sea currents is the direction of movement. We know that sea waves and sea currents are mass movements of water (read more : Understanding Seawater Motion: Benefits ). But both are very different. Surface currents vs. Deep currents by Cedric Wright Surface currents vs. Deep currents Occur in water Are caused in three ways Used in oceans currents moving water can (on occasions) can go deep into water Deep Currents Surface Currents Both Movements deep inside water Carries cold water becomes warm movements on the surface of
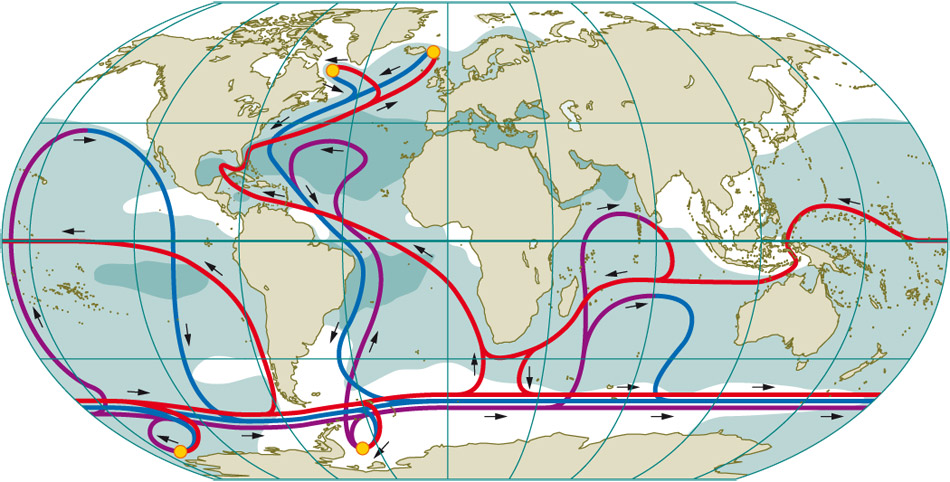
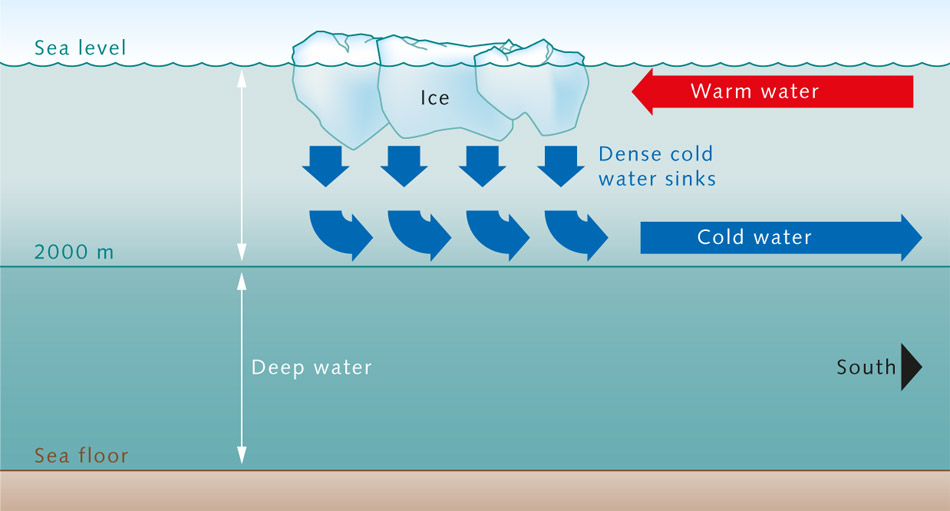
Thermohaline Circulation - Currents: NOAA's National Ocean ... Winds drive ocean currents in the upper 100 meters of the ocean's surface. However, ocean currents also flow thousands of meters below the surface. These deep-ocean currents are driven by differences in the water's density, which is controlled by temperature (thermo) and salinity (haline). This process is known as thermohaline circulation.
Earth's Waters 4-4 Notes Flashcards - Quizlet Compare and contrast surface currents and deep currents. They are both are moving water that flows through oceans. Surface currents are towards the top of the ocean, can be warm or cold, and are controlled by winds. Deep currents are low, deep in the ocean, cold, and are controlled by density. How does upwelling effect marine life?
PDF Ocean Surface Currents - 6th grade science which affect both surface and deep currents. These movements are essential to stirring the ocean, delivering oxygen to depth, distributing heat, and bringing nutrients to the surface. Stratification occurs when surface waters and deep waters are separated into layers by distinct differences in
PDF Ocean Currents and Sea Surface Temperature Part I: Obtain maps of sea surface temperature (SST) and ocean surface winds from the Live Access Server. 1. Click on the link for the Live Access Server. 2. Click on 'Choose Dataset' if it does not automatically appear. Select Oceans, Daily Sea Surface Temperature (GHRSST). 3. For region, have students select their own from the drop-down menu.
Ability Scores – 5th Edition SRD But adventurers often face dense forests, deep swamps, rubble-filled ruins, steep mountains, and ice-covered ground—all considered difficult terrain. You move at half speed in difficult terrain —moving 1 foot in difficult terrain costs 2 feet of speed—so you can cover only half the normal distance in a minute, an hour, or a day.
What are the differences between surface currents and deep ... Surface currents are different from deep ocean currents because surface currents depend on the temperature, pressure, wind, and moon to determine them but deep water currents are too deep for any ...
Effect of Surface Currents | manoa.hawaii.edu ... Deeper water tends to be higher in oxygen than the warmer surface water because gasses such as oxygen dissolve better in colder water. It is also higher in nutrients because the higher oxygen levels allow bacteria to cycle important nutrients such as nitrate and phosphate from decomposing organic matter.
In one or two paragraphs, compare and contrast surface ... Surface currents refer to movement of the top layer of ocean water. Surface water flows in to replace the sinking water, which in turn becomes cold and salty enough to sink. examples of surface ocean currents are California Current (Cal) in the Pacific ocean basin and the Canary Current (Can) in the Atlantic ocean basin. Deep ocean currents
Marine Definition & Meaning - Dictionary.com Marine definition, of or relating to the sea; existing in or produced by the sea: marine vegetation. See more.
8(q) Surface and Subsurface Ocean Currents Surface Currents of the Subtropical Gyres On either side of the equator, in all ocean basins, there are two west flowing currents: the North and South Equatorial ( Figure 8q-1). These currents flow between 3 and 6 kilometers per day and usually extend 100 to 200 meters in depth below the ocean surface.
Earth - Wikipedia This gives an apparent movement of the Sun eastward with respect to the stars at a rate of about 1°/day, which is one apparent Sun or Moon diameter every 12 hours. Due to this motion, on average it takes 24 hours—a solar day—for Earth to complete a full rotation about its axis so that the Sun returns to the meridian. The orbital speed of ...
Ocean currents | National Oceanic and Atmospheric ... tides and currents. Ocean water is on the move, affecting your climate, your local ecosystem, and the seafood that you eat. Ocean currents, abiotic features of the environment, are continuous and directed movements of ocean water. These currents are on the ocean's surface and in its depths, flowing both locally and globally.
What is the difference between how surface currents and deep ... What is the movement of deep currents? — These deep-ocean currents are driven by differences in the water's density, which is controlled by ...
What is the difference between surface and deep currents 16 Dec 2021 — A. Surface currents move much more slowly, while deep currents travel quite quickly. B. Deep currents are driven by density differences, while ...
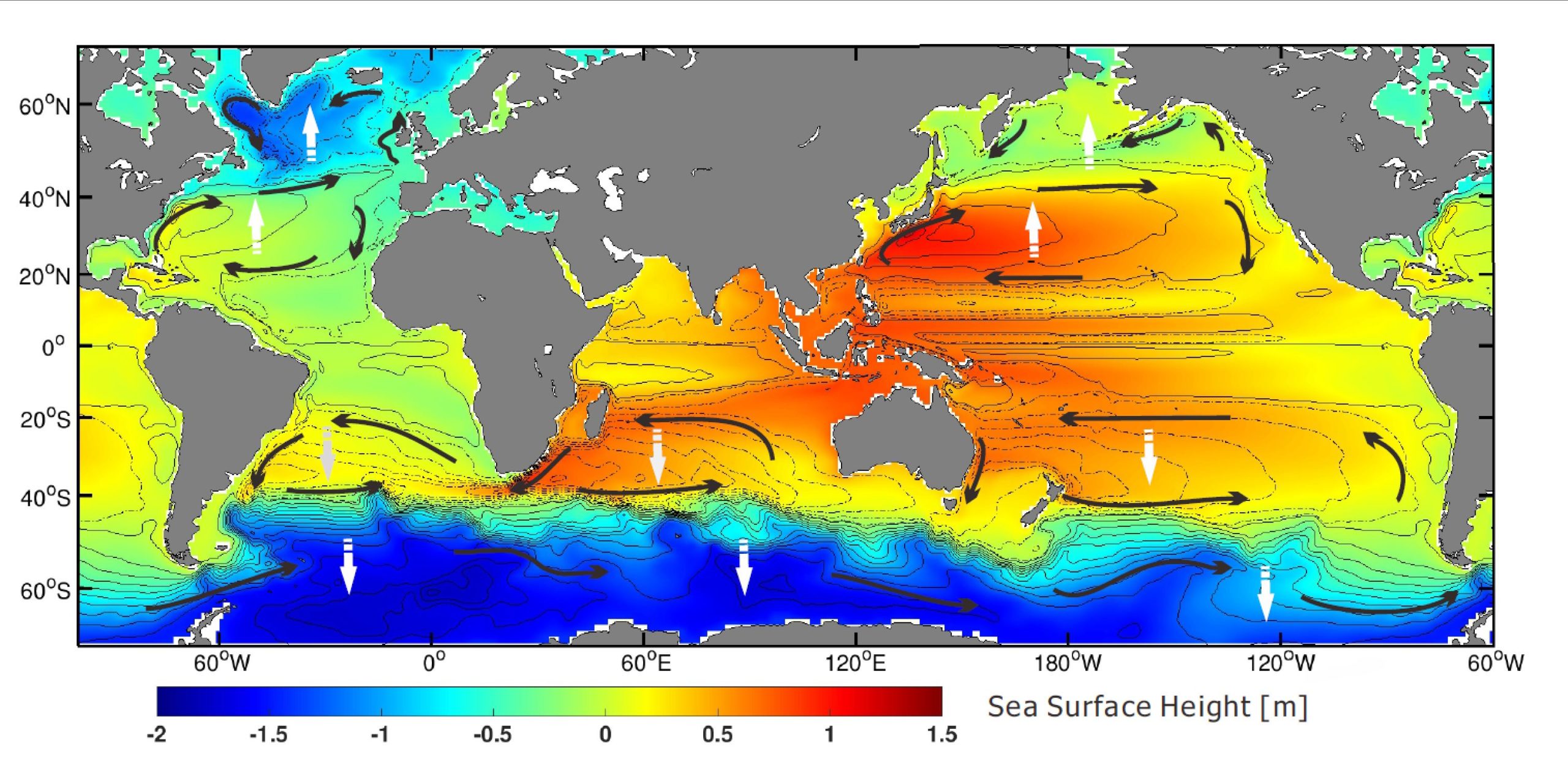
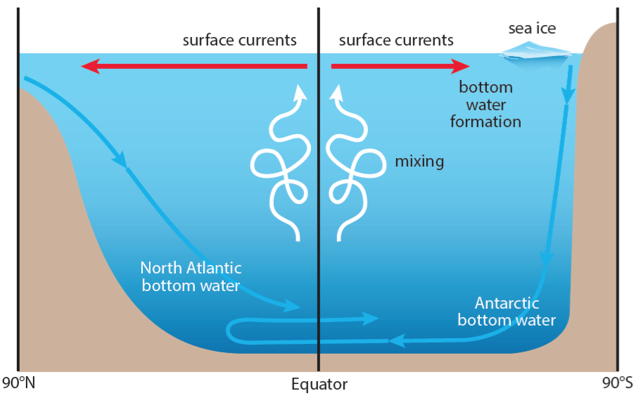
Ocean Circulation: Surface Water and Deep Water | Earth ... The colors are a bit hard for me to see, but note that in the North Atlantic, a surface current flows north and a deep current flows south. This means that deep water forms in the North Atlantic. It's important to appreciate that any Figure drawn at this scale, the entire ocean, is approximate.
Understanding Surface Currents vs Deep Ocean Currents Deep currents are driven by temperature and water density/salinity. Of course, deep currents impact surface currents, which carry warm water to the poles. Surface currents are also driven by global wind systems fueled by energy from the sun. Factors like wind direction and the Coriolis effect play a role.
Two Types of Ocean Currents - Sciencing 23 Apr 2018 — Surface currents refer to movement of the top layer of ocean water – the upper 330 feet or so – primarily driven by wind. The large-scale ...
What are 2 differences between surface currents and deep ... 18 Jan 2021 — Deep ocean currents known as density currents are different from surface currents in that the driving force is gravity and not the winds.
Currents | Earth Science - Lumen Learning Surface currents can flow for thousands of kilometers and can reach depths of hundreds of meters. These surface currents do not depend on weather; they remain unchanged even in large storms because they depend on factors that do not change. Surface currents are created by three things: global wind patterns the rotation of the Earth
Ocean Surface Currents | manoa.hawaii.edu ... Surface currents are only 50 to 100 meters deep (Table 3.1). Though shallow, they are extremely important in determining the world's weather and climates, and in distributing the ocean's heat and nutrients. Winds are described by the direction from which they blow, whereas water currents are described by the direction toward which they flow.
PDF CHAPTER SECTION 1 Currents - WPMU DEV Not all ocean currents are found at the surface. Movements of ocean water far below the surface are called deep currents. Unlike surface currents, deep currents are not controlled by wind. Deep current move-ments are controlled by water density. Density is the amount of matter in a given space or volume. The density of ocean water is affected by




























0 Response to "41 compare the movement of surface and deep currents"
Post a Comment